Run Linux ELF binary file on Android
Although usual Android apps are installed to your device as APK files, you still have the option to run native ELF binary file compiled for the architecture of your device.
Prerequisites
- A Linux PC with gcc or other C compiler installed
- If you are trying to run the compiled ELF file on a device with an ISA that differs from your PC, a cross compiler is required
- The most common scenario is x86-64 PC + ARM64 (aka. AArch64) Android device, where
aarch64-linux-gnu-gccis needed
- The most common scenario is x86-64 PC + ARM64 (aka. AArch64) Android device, where
- If you are trying to run the compiled ELF file on a device with an ISA that differs from your PC, a cross compiler is required
- An Android phone, container or emulator (I am using Waydroid) with Termux installed
Compilation
Take the following "Hello world" program (test.c) as an example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello world!\n");
return 0;
}Use gcc to compile it:
gcc test.c -static -o testIf you intend to run the compiled binary on ARM64 (aka. AArch64) devices and your PC is not ARM64:
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc test.c -static -o test-static option is needed to statically link the system C library as Android uses bionic as C library instead of glibc or musl.
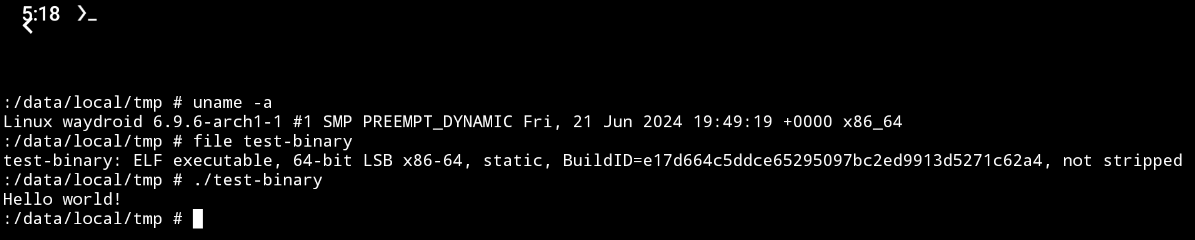
Next, copy the compiled ELF file to your Android device.
Copy the compiled ELF file to the appropriate path
As /storage is mounted with option noexec, you can't execute files under the /storage directory even if they have been given executable permission with chmod +x. Therefore, we need to find a directory without noexec mounting option. A common choice is /data/local/tmp.
- $ mount
...
tmpfs on /storage type tmpfs (rw,nosuid,nodev,noexec,relatime,mode=755,gid=1000,inode64)
...To access /data/local/tmp directory, the root permission is needed for Termux.
su
cp test /data/local/tmpExecute the file
chmod +x test
./test